Home Product Center Common Defects in Heat Treatment
Common Defects in Heat Treatment
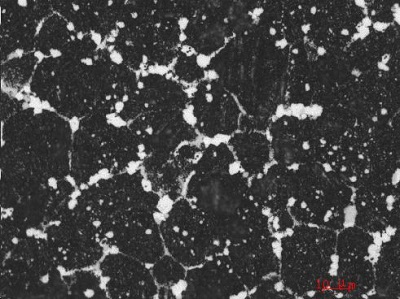
Overheating: In metallographic structure, there are coarsening grains, and the quantity, shape and distribution of carbide have changed. This is characterized by: the quantity of carbide is decreasing gradually; according to the different levels of overheating, the shape of carbide will be shown as adhesion, trailing and the phenomenon of transiting from equiaxed shape to angularity. Incontinuous reticulation or reticulation will be seen along the grain boundary (Picture 1).
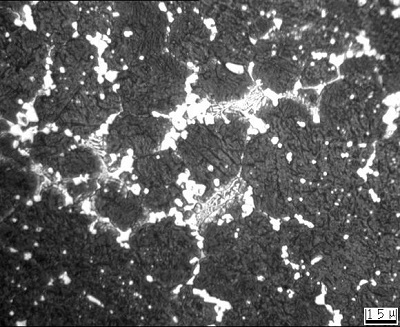
Overburning: In metallographic structure, ledeburite eutectic structure is seen on grain boundary. It is distributed in blocks or semi-reticulation (Picture 2). Meanwhile, black structure perhaps arises.
Quenching distortion: There are 3 kinds of quenching distortions: dimension change, shape change and twist, mainly because of the superposition of heat stress and structure stress during the quenching process.
Quenching cracking: Quenching cracking mainly occurs at the quench-cooling process. In this process, the stress of the work piece increases with the decrease of temperature, while the plasticity also decreases with it until martensite appears, then the plasticity is almost zero. So the quenching cracking phenomenon is caused by the formation of the brittle phase martensite.
Poor hardness: After quenching and tempering, if the hardness of high speed steel tool is lower than the standard requirement level, then this is known as poor hardness. Meanwhile, when the hardness is too high, the problem of decreased toughness should be also considered.
Insufficient tempering: During the tempering process, insufficient tempering is caused by the low tempering temperature, insufficient heat preservation or insufficient tempering frequency. Insufficient tempering should be paid much attention, as this could easily lead to many defects in heat treatment.
 |
 |
|
|
Picture 1, overheating structure (Level 5, 500X) |
Picture 2, overburning structure (500X) |
